Process Simulation for Decarbonization: From Insight to Industrial Transformation
How Fives ProSim’s process simulation software contributes to reducing carbon footprints in process industries
Decarbonization has become one of the defining challenges for industry. Energy-intensive sectors such as chemicals, refining, and metallurgy must not only reduce their greenhouse gas emissions, but also adapt to a rapidly evolving energy landscape. Meeting these goals requires both incremental efficiency gains and transformative changes in the way processes are designed and operated. Process simulation has emerged as one of the most effective enablers to support this transition.
Understanding Complexity through Simulation
Industrial processes involve a multitude of physical and chemical interactions: thermodynamics, reaction kinetics, transport phenomena, and operational constraints. Empirical approaches, while practical in some cases, often fail to capture this complexity.
Fives ProSim’s process simulation software provides engineers with a rigorous framework to model and analyze process behavior. By combining accurate thermodynamic models with flexible flowsheeting environments, they enable the prediction of performance across a wide range of conditions. This predictive capability is critical when industries explore low-carbon pathways that are not yet commercially mature.
Identifying Energy and Carbon Hotspots
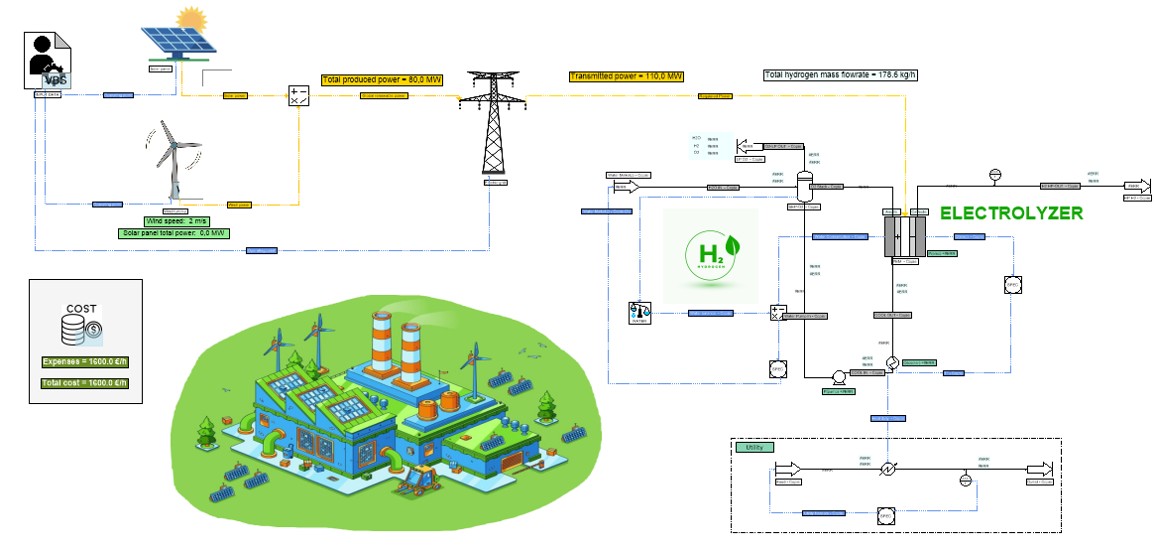
A key step in any decarbonization strategy is to quantify emissions and locate inefficiencies. Process simulators can integrate material and energy balances over the entire flowsheet, making it possible to pinpoint the “hotspots” of carbon intensity. These might include units operating far from optimal efficiency, energy recovery opportunities, or streams that could be valorized.
By providing a transparent and quantitative view of process performance, simulation creates a reliable foundation for deciding where to act first.
Exploring Alternative Energy and Feedstocks
The transition to low-carbon industry often involves alternative energy carriers and raw materials. Hydrogen, renewable electricity, or bio-based feedstocks are all gaining attention, but their integration into existing assets poses technical challenges.
With tools like ProSimPlus or Simulis Thermodynamics, engineers can test scenarios virtually before committing to physical trials. For instance, the partial substitution of natural gas by hydrogen in a reforming or combustion unit can be simulated to evaluate its impact on efficiency, emissions, and downstream performance. Similarly, incorporating biomass-derived intermediates into petrochemical processes can be assessed in terms of yields, by-products, and carbon footprint.
Simulation thus reduces uncertainty and accelerates the safe adoption of sustainable solutions.
Supporting Process Intensification and Innovation
Decarbonization is not only about substitution. It also demands new process concepts. Process intensification, such as membrane reactors, reactive distillation, or advanced heat integration, promises significant energy savings but requires robust predictive models for design and scale-up.
Here, advanced simulators provide essential support. By coupling detailed thermodynamics with flexible process modeling, software platforms help researchers and engineers design intensified processes that are both efficient and technically sound. This accelerates the transition from laboratory-scale ideas to industrial deployment.
Bridging Engineering, Economics, and Sustainability
Simulation also connects the technical level with broader decision-making frameworks. By linking process models to life cycle assessment, techno-economic analysis, or carbon accounting, companies gain an integrated view of their decarbonization strategies.
This holistic perspective is increasingly important as policy instruments such as carbon pricing and emissions trading influence industrial competitiveness. The ability to quantify trade-offs between environmental impact and economic performance ensures that investments in decarbonization are both ambitious and sustainable.
Decarbonization is not a single milestone but an ongoing transformation of industrial systems. Achieving it requires tools that combine scientific rigor with practical usability. With its complete range of simulation software and over 30 years of experience, Fives ProSim exemplifies how advanced modeling can help industries understand, optimize, and reimagine the way to design and operate their processes.